
How Data Acquisition Helps Your Quality Assurance
There's certainly no dearth of variety when it comes to electronic test and measurement devices. From general-purpose instruments like multimeters and oscilloscopes to highly specialized equipment for specific industries, there is a correct tool for every need.
However, there is one group of test devices that stand tall in this crowded field because of their power and versatility. They are the data acquisition systems.
In this article, find out what makes them so special, which industries use them, and how they work. Let's start with the basics.
What is data acquisition?
Data acquisition (DAQ) is the systematic measurement and recording of electrical characteristics or physical metrics with one of these end goals:
- design verification
- electrical or thermal characterization
- monitoring of an electronic, manufacturing, or physical process
- control over the testing of a product
What are data acquisition systems?
A data acquisition system consists of purpose-built hardware and software that equip it to acquire data from a device under test (DUT) for verifying its design, improving its operations, and boosting its reliability.
A data acquisition system allows engineers to measure and collect data such as the electrical characteristics (like voltages and currents) of a DUT in different scenarios, along with measurements of its surrounding or external physical phenomena (like temperature, pressure, or sound levels).
On the face of it, measuring electrical characteristics or physical phenomena doesn't sound impressive. After all, other instruments like digital multimeters, LCR meters, or optical power meters also do that. But a DAQ system is nothing like them.
Let's look at the characteristics that make a DAQ system stand out from other test and measurement instruments.
What makes data acquisition systems special?
The typical data acquisition system has the following features that make it a compelling and versatile testing solution for many industries.
1. Scalability

Fig 1. Two Keysight DAQ systems with three slots each. Each slot can take one of the 20/40-channel modules shown on the right, enabling measurement of up to 120 signals simultaneously.
The most unique aspect of a DAQ system is its scalability. A typical DAQ system is equipped with anywhere from tens to even hundreds of measurement channels. It can simultaneously measure a large number of signals from a large number of DUTs (or a large number of test points on a few DUTs). It supports switching and multiplexing to choose between different sets of inputs or devices based on the test plan.
The illustration below shows DAQ scalability using multiple input modules, each supporting dozens of input channels.
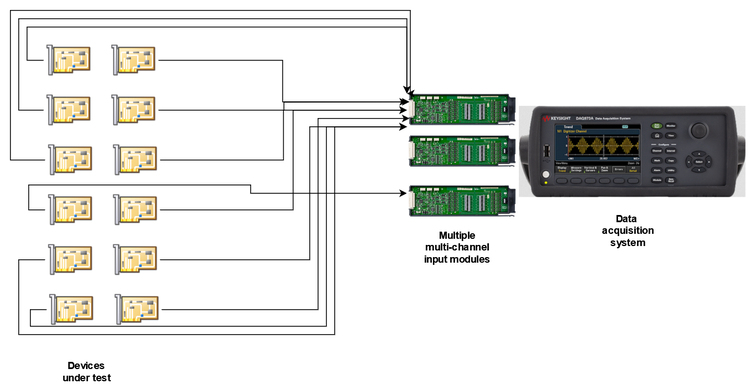
Fig 2. Scalable testing using data acquisition system
2. Ability to measure a variety of signals
A data acquisition system can measure a variety of signals like:
- direct currents (DC) and voltages
- alternating currents (AC), voltages, frequencies, and periods
- resistances, either two-wire or the more accurate four-wire
- capacitances
- temperature measurements
- vibration forces via sensors like accelerometers
A DAQ system typically has a built-in high-precision digital multimeter circuit as well as other custom measurement circuits for these signals.
3. Designed for automation
A data acquisition system is purpose-built for bulk automated testing and quality control on production lines. Automated test sequences are supported.
4. Configurability
Aspects like the number of active channels, the sampling rate per channel, and the type of signal at each channel are all configurable via the DAQ software.
Measurements must often be timed correctly with specific events and trigger conditions. The DAQ software enables such synchronization.
5. Real-time data analysis and visualization
Data acquisition systems enable real-time processing and analysis of data, enabling immediate diagnosis and analysis. They also calculate and record derived metrics obtained by specifying formulas in the DAQ software. For example, a power metric can be recorded based on the readings from the voltage and current channels of each DUT.
6. Recording and storage
A DAQ system supports the immediate recording of data to a local storage device as well as the network transmission of data to a computer for remote storage. The latter enjoys all the benefits of computer-based storage, such as large capacities, high speeds, and redundancies.
7. Signal conditioning
Since input analog signals may not be directly suitable for recording, a good DAQ system provides signal conditioning circuitry like amplification, filtering, and linearization for each input channel. Some data acquisition systems even support configuring and deactivating each component of their signal conditioning pipelines.
8. High speed and high throughput
DAQ systems enable high-speed, high-throughput, automated bulk testing of devices. They complement manual quality control using other instruments like digital multimeters and oscilloscopes.
What are some real-world applications of data acquisition?
Here are some of the data acquisition applications in different industries.
Aerospace and defense
When testing an avionics or weapons subsystem, a data acquisition system is connected to all the test points of the dozens of constituent electrical circuits. They may also be connected to multiple physical sensors in the mechanical or hydraulic subsystems. The subsystem is then subject to testing conditions like wind conditions or interference, and the DAQ system is used to record a variety of electrical and physical characteristics.
Automobiles
Automobiles contain a variety of components like the controller area network (CAN) bus, dashboard switches, battery charging system, engine controls, engine sensors, external sensors, and more. A data acquisition system is connected to all these subsystems to collect the wide variety of signals they produce — electrical, electromagnetic, mechanical, acoustic, thermal, and more.
When tests like on-road tests or crash tests are conducted, the DAQ system records all this data. Engineers later analyze the data for any reliability or safety problems as well as optimization opportunities.
Consumer appliances and devices
The behaviors of consumer appliances and smartphones are characterized using data acquisition systems. The test points of their power supplies, battery charging circuits, mainboards, and temperature sensors are connected to a DAQ system. Characteristics like voltages, impedances, radio interference, or battery drain are measured using the DAQ system while the appliance is operated under different environmental conditions.
What sensors are commonly used with DAQ systems?
DAQ systems acquire data using sensors. Common sensors include:
- Thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), or thermistors to measure temperatures
- Transducers that convert physical forces into electrical signals, such as accelerometers for vibration data and microphones for acoustic data
- Strain gauges to measure stresses in physical structures
- Photodiodes to measure changes in optical signals
What factors should you consider when selecting a data acquisition system for a specific application?
When selecting a DAQ system for your application and industry, here is a minimum set of questions to ask:
- How scalable should it be? How many DUTs and signals should it record, i.e., how many channels should it have?
- What should be the minimum sampling rate for each test scenario?
- What sensors do your DUTs need, and is the DAQ system compatible with all of them?
- Is the DAQ system modular and expandable for your project's future needs?
- Can it interface with your computing and data storage systems?
- Does the DAQ hardware have a calibration certificate and a regularly scheduled calibration path, especially if high measurement accuracy and traceability are critical?
What is the significance of sample rate and resolution in data acquisition?
The sample rate determines how often a signal is measured, which is crucial for capturing fast-changing signals. A high sampling rate ensures that rapid fluctuations in real-world signals are not lost but accurately represented in the stored data. The frequency of sampling must be sufficient to capture the dynamics of the real-world phenomenon.
In addition, if you have a high channel count, ensure that the data acquisition system can handle the increased flow of information due to a high sampling rate without compromising speed or accuracy.
The resolution affects the granularity and precision of the measurements. A higher resolution provides more detail, which may be critical for later analysis.
What are the key components of a typical data acquisition device?
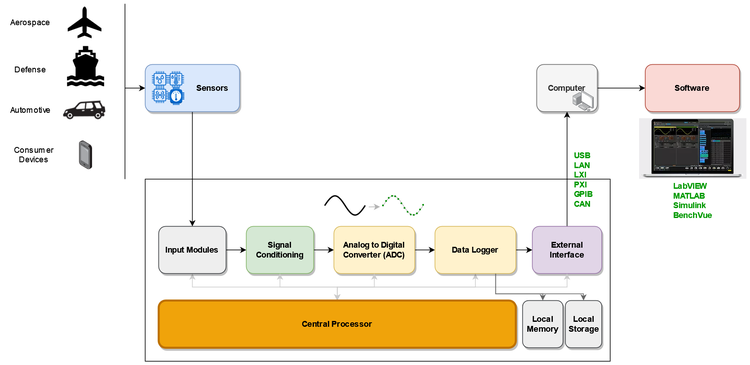
Fig 3. Components of a data acquisition system
The key components of a DAQ device are:
- Power supply: This supplies reliable power to the mainboard and modules.
- Input modules: The input modules contain the channels that receive signals from the DUT and its sensors. Some modules have switching and multiplexing capabilities to route the signals from a shared set of sensors to different test devices.
- Central processor: This is the control system of the DAQ, processing data according to the configuration and ensuring that all operations are done correctly in the proper order.
- Signal conditioning circuitry: Analog signals are often susceptible to noise. For example, sensors such as accelerometers can produce very noisy data. Such data must be cleaned up and free of distortions for reliable data analysis.This subsystem ensures that all the analog input signals are compatible with the downstream processing components of the DAQ device. It consists of components like amplifier circuits, low-pass filters, and high-pass filters to suppress noise. Linearization circuits help correct the nonlinear response curves and improve the accuracy of certain sensors like strain gauges.
- Analog-to-digital converter (ADC): This samples the clean analog signals coming from the signal conditioning circuits and digitizes the signal levels into dimensionless integers. The central processor then converts the digital signals to real numbers with the correct units based on the respective channel's configured signal type and measurement range.
- Data logger: The data logging subsystem records the digital data in temporary memory and local storage devices and transmits them to the connected computer.
- External interfacing subsystem: This subsystem talks to the connected computer via protocols like the peripheral component interconnect (PCI), universal serial bus (USB), ethernet (LAN), or the general purpose interface bus (GPIB).
What role does software play in data acquisition, and what features are essential in data acquisition software?
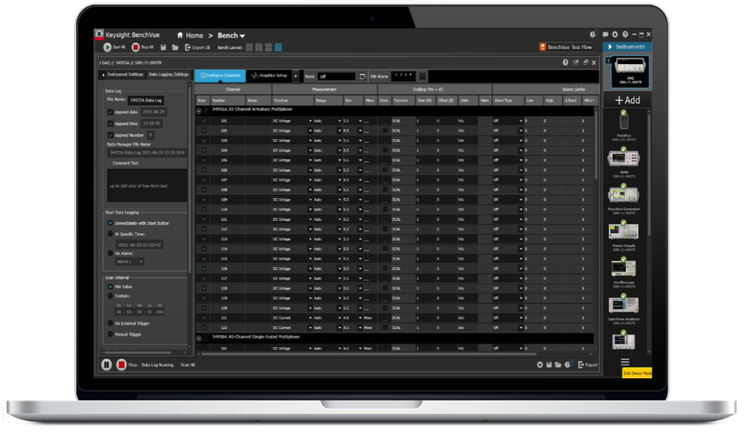
Software plays a critical role in data acquisition systems. All the special characteristics of data acquisition systems we described earlier are possible only because of software.
There are two pieces of software at play:
- the embedded software (or firmware) that runs on the DAQ device
- the application software that runs on the connected computer
Both are crucial for each special feature of a DAQ system. Some features that must be considered essential are:
- Great user experiences: The configure-measure-record-visualize sequence on the device and the computer must be smooth, fast, and intuitive experiences for users.
- High level of configuration automation: Both the embedded and the application software must provide a high level of configuration automation of channels, signal types, ranges, trigger conditions, and other measurement aspects.
- Sophisticated data analysis and visualization: The software, particularly the application on the computer, must enable users to easily organize and visualize vast quantities of recorded data so that they can draw the insights hidden in the data.
- Predefined test plans for different industries: Good software must come with predefined test plans for different industries (and provide downloads for on-demand installation). This helps save a lot of time and avoid mistakes.
There are many data acquisition software environments for implementing data acquisition applications, including:
- Keysight PathWave Test Automation
- MATLAB/Simulink
- Keysight's PathWave BenchVue
General-purpose programming languages like Python, C, and C++ with DAQ-specific libraries are also commonly used for real-time data collection, data analysis, and measurement applications.
Scalable reliable testing with data acquisition systems
In this article, we got an overview of data acquisition systems and what makes them special among other test and measurement instruments.
Keysight has more than two and a half decades of experience in building modular, high-speed, high-throughput data acquisition systems for aerospace, defense, automotive, telecommunication, and consumer device industries.
Contact our experts for help with selecting the right data acquisition system for your business and project.